Melting furnace (induction heating)

No crucible, so
Reduce contamination to the limit
High-purity crystal growing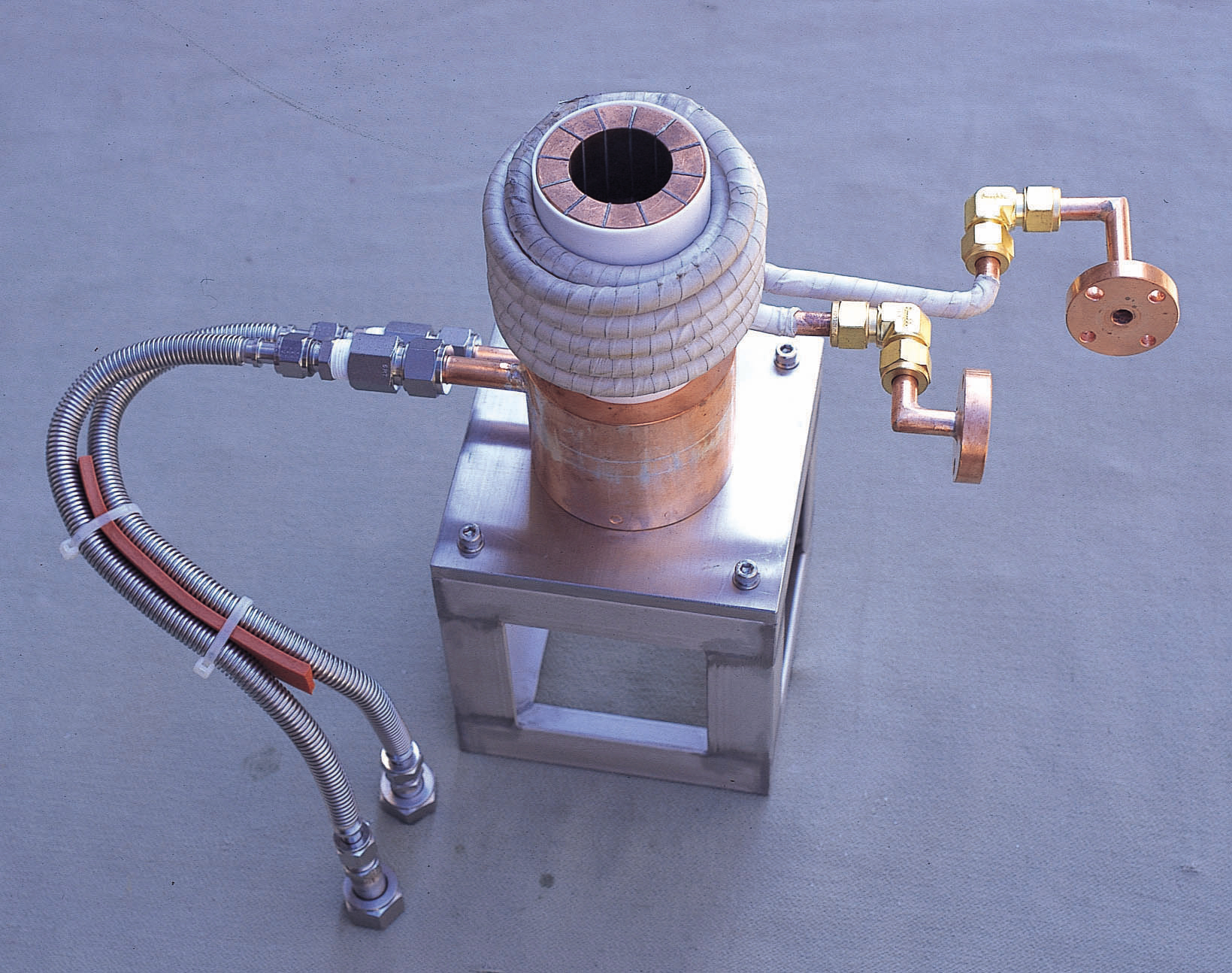
Description
Floating melting is a production method used to obtain high-purity conductive materials. It involves applying high-frequency output to conductive materials for heating and melting, while suspending the material using the frequency and eddy currents generated by a high-frequency induction heating power supply.
Floating melting techniques include cold crucible melting and levitation melting.
Feature
- No crucible, so no impurities are mixed in from the crucible wall.
- No crucible, so cost of consumables reduces.
- No reaction with the crucible material, so fluxes with a wide variety of ingredients and compositions can be used.
- Promote the refining reaction of metals by utilizing the active stirring force of the molten metal by electromagnetic force.
- Easy melting of high-purity metals and refractory metals
Cold crucible melt
This melting method has a water-cooled copper crucible inside the work coil, and a conductor is placed in it to heat it.
When the power of high-frequency induction heating is applied to the work coil, an eddy current opposite to that of the work coil is generated in the water-cooled crucible.
The eddy current of the work coil is applied to the conductive material and heating and melting proceed, but the eddy current of the copper rut and the electromagnetic repulsive force of the eddy current of the work coil act to float.
Levitation melting
Application
◆ Oxide crystals
◆ High-purity metals and alloys
◆ Silicon
Specification
| Heating method | High frequency induction heating |
|---|---|
| Heating temperature | 1700℃ |
| Ultimate vacuum | 5×10-4Pa |
| Atmosphere | Vacuum or inert atmosphere or air |
| Melting amount | 10kg (cold crucible melting), 100g (levitation melting) ※as iron |
| Control method | Touch panel |
| Heatinf control | Temperature or power control |
| Data output | Data recorder・PC |
| Industrials |